
Cybersecurity Reporting: transparency in digital danger
Home » Security » Cybersecurity Reporting: transparency in digital danger
Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Incident reporting is an essential part of an effective security strategy. Tracking events is crucial not only to understand the nature and extent of attacks, but also to ensure transparency and comply with regulations.
One such important regulation is NIS2. Want to know more about this directive? Then take a look at these blogs:
What is Incident Reporting
Incident Reporting in Cybersecurity is capturing the details of an incident, such as a click on a phishing link, at the time it happens or shortly afterwards. These details are then used to assess and prioritise the risk level of the incident. Tools such as Microsoft Defender assign a label that determines how serious the event is.
Afterwards, you can see a detailed summary of the entire event. The idea is for a team of cybersecurity experts to check these reports. This is because they also contain many so-called false positives. That is, sometimes the alarm is raised too quickly and an event is seen as a threat when it is not. With knowledge and skill, the right measures are taken to deal with the incident and prevent it in the future.
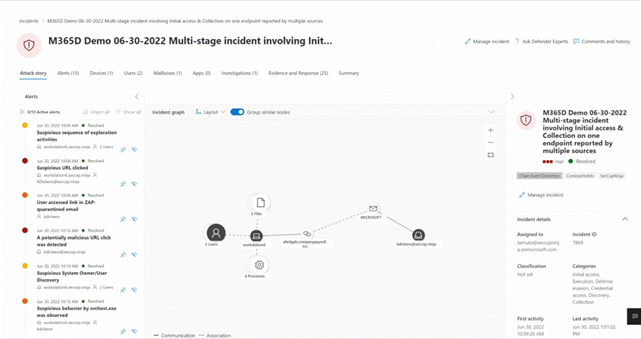
Why incident reporting?
Incident Reporting is not just about capturing cyber incidents; it is also about detailed documentation of the events and possible preventive measures for the future. This is vital for several reasons:
There are several reasons why it is vital:
- Understanding the nature of cyber attacks: By tracking incidents, organisations gain a deeper understanding of the methods and tactics used by attackers. This insight is essential to prevent future attacks and implement proactive defence measures.
- Build trust: Implementing incident reporting in your IT infrastructure helps build trust with stakeholders. Think of your customers, partners and regulators. It shows that, as an organisation, you are open to accountability and willing to learn from any risks.
- Compliance with regulations and standards: Many regulations and industry-specific standards require organisations to be able to adequately track and process incidents. By including the ability to submit transparent reports, you comply with these requirements. This way, you avoid fines or other legal consequences
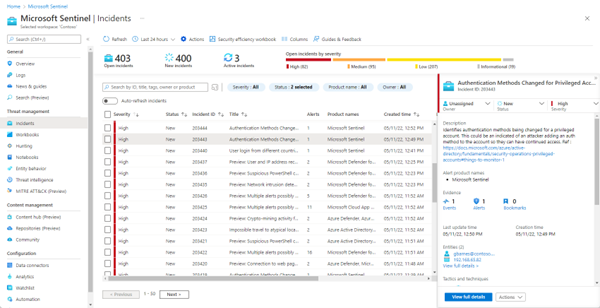
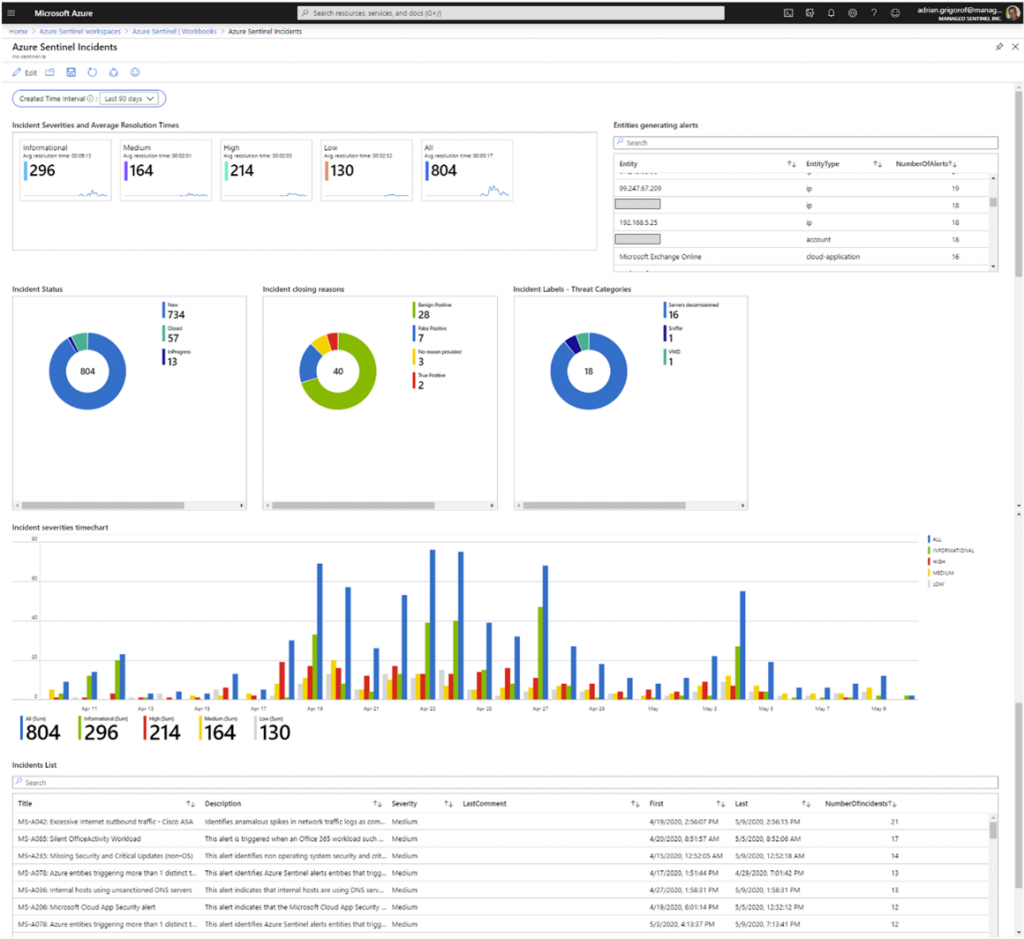
The different components of Incident Reporting within your organisation
- Detection
Goal: Recognising unusual activities that may indicate a security incident.
- Methods: Use of intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and regular security audits. Microsoft offers this with Defender and Sentinel. From the Microsoft Business Premium licence, you enjoy an incident reporting tool.
- Importance: Early detection is crucial to minimise the impact of an incident.
- Reporting
Goal: Documenting and communicating incidents.
- Procedure: Preparation of a detailed report describing the nature, extent and potential impact of incidents.
- Communication: Inform the incident response team, management, and if necessary, external parties such as law enforcement agencies.
- Analysis
Purpose: Investigating the incident to determine its cause, extent and impact.
- Steps: Collect evidence, analyse log files, and examine the systems and networks involved.
- Outcome: A clear understanding of how the incident could have happened and which systems were affected.
- Reducing damage
Aim: Taking measures to limit damage and prevent further spread.
- Actions: Isolate affected systems, temporarily disable certain services, and apply emergency patches.
- Strategy: Ensure that the incident does not cause further damage to the organisation or its stakeholders.
- Recovery
Purpose: To restore affected systems and services to their normal status.
- Processes: Cleaning up affected systems, restoring data from backups, and gradually bringing services back online.
- Verification: Testing that all systems are back up and running properly and that security measures are effective.
- Evaluation
Purpose: To assess incident response and update security measures and procedures.
- Learnings: Identifying what went well and what went less well during the response.
- Improvements: Adapting the incident response plan and strengthening the security infrastructure to prevent future incidents.
Are you interested in transparent cybersecurity reports? Talk to one of our specialists free of charge to discuss your solution together!
Talk with an expert today!